A fuel temperature sensor is a component in a vehicle’s fuel system that monitors the temperature of the fuel. It plays a crucial role in ensuring the proper operation and performance of the engine. Here’s an explanation of its function and common failure symptoms:
Function:
The primary function of a fuel temperature sensor is to measure the temperature of the fuel as it flows through the fuel system. The sensor typically consists of a temperature-sensitive element, often a thermistor, and it is connected to the vehicle’s engine control unit (ECU) or engine management system. The ECU uses the data from the fuel temperature sensor to make real-time adjustments to the engine’s air-fuel mixture, ignition timing, and other parameters to optimize engine performance and emissions. Here’s how it works:
- Optimizing Combustion: Fuel temperature can affect the vaporization and combustion characteristics of the fuel. Colder fuel may not vaporize efficiently, leading to incomplete combustion, while overly hot fuel can cause knocking and poor performance. The sensor provides information to the ECU so that it can make adjustments for optimal combustion.
- Cold Start Enrichment: The sensor’s data is crucial during cold starts. Cold fuel needs a richer air-fuel mixture for efficient combustion. The ECU uses the fuel temperature data to adjust the mixture for cold start conditions.
- Emissions Control: Monitoring fuel temperature also aids in reducing emissions. By adjusting the air-fuel mixture based on fuel temperature, the engine can produce fewer pollutants.
Failure Symptoms:
When a fuel temperature sensor fails or malfunctions, it can lead to various issues, including:
- Poor Fuel Economy: A faulty fuel temperature sensor may provide inaccurate data to the ECU, leading to an incorrect air-fuel mixture. This can result in decreased fuel efficiency and poor gas mileage.
- Rough Idling: Incorrect fuel temperature data can cause the engine to idle roughly or even stall.
- Engine Performance Problems: The sensor’s failure may lead to reduced engine power, acceleration issues, or an overall decrease in performance.
- Check Engine Light (CEL): A malfunctioning fuel temperature sensor can trigger a check engine light (CEL) and store diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the sensor’s performance.
- Cold Start Issues: During cold starts, the engine may have difficulty starting or may not run smoothly if the sensor is not providing accurate data for cold start enrichment.
- Emissions Problems: A malfunctioning fuel temperature sensor can result in increased emissions, potentially causing a vehicle to fail emissions tests.
- Detonation or Knocking: Inaccurate fuel temperature data can lead to engine knocking or detonation, which can damage the engine if not addressed.
If you experience any of these symptoms or suspect a problem with the fuel temperature sensor, it’s advisable to have the sensor tested and, if necessary, replaced by a qualified mechanic. They can use diagnostic equipment to assess the sensor’s performance and ensure that it is providing accurate data to the engine control unit. Replacing a faulty sensor can help restore proper engine operation and efficiency.
]]>The cross ply tyre
This type of tyre has been around since 1888. The tyres were invented by John Boyd Dunlop and were first used on a bicycle. The pneumatic design is constructed using a network of interlocking nylon cords, which are layered diagonally across each other at a 45-degree angle to the centre line of the wheel. Along with the tough outer rubber shell, their construction increases the strength and rigidity of the sidewalls. This makes the sidewalls more resistant to wear and tear. This is important for protecting the inner inflated tube which is made from a soft rubber and prevents air loss. If the tube gets punctured, it will result in a flat tyre.
The radial tyre
As mentioned above, radial tyres were introduced over half a century later as a more flexible alternative to their cross ply predecessors. They use steel cords instead of nylon ones, as well as steel belts to support the tread of the tyre. In a radial ply tyre, the cords overlap and are positioned at a 90-degree angle to the wheel’s centre line. The advantage of this design is that the flexibility and strength of the tyre allow it to absorb shocks and impacts more effectively, maintaining contact with the road and generating less heat. Moreover, this construction does not require an inner tube.
If your radial or cross ply tyres are badly punctured or the tread has been worn down, you can easily compare the prices of Michelin tyres and those from other popular brands online. Both types vary in complexity, but it may be possible to repair the tyre using either a sealant or cross ply repair patches, for example.
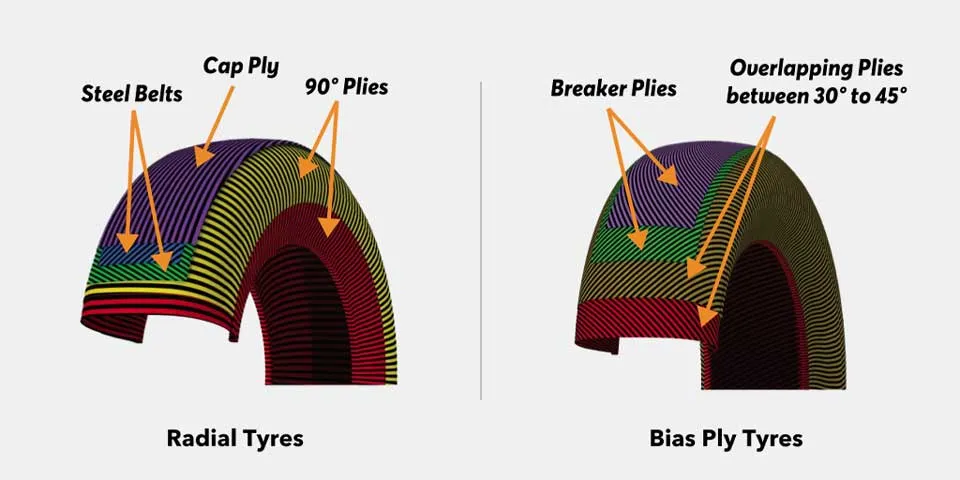
Radial vs Cross Ply
Cross ply tyres: advantages and disadvantages
- High resistance to sidewall damage
- Cheaper to produce
- Improved vehicle stability in certain driving/working environments
- Lower fuel efficiency
- Reduced driving comfort due to tyre rigidity
- Poor heat dissipation, causing the tyre to wear faster
- A low speed rating, more likely to blow out at high speeds
Radial tyres: advantages and disadvantages
- Improved road contact and vehicle handling
- Improved fuel efficiency
- Improved driving comfort due to flexibility
- A higher speed rating
- Higher resistance to tread wear and less risk of a loss of traction
- The sidewalls are more vulnerable to damage caused by collisions
- Less effective at handling minor bumps in the road due to steel belt
Safety
Under no circumstances should you use tyres with two different constructions on the same axle. It is highly advisable to stick to one type of tyre for both axles for safety reasons related to vehicle stability and weight distribution. In cases where mixing tyres is unavoidable, it is recommended that cross ply tyres are fitted to the front axle and radial ones are fitted at the rear.
Making sure the tyre tread depth complies with safety regulations is also critical. If the tread is too worn, it could cause a loss of traction and result in an accident. This is especially dangerous in wet driving conditions. If you need to replace your tyres quickly and affordably, you can easily select and buy cheap car tyres online.
Related products
Tools and Materials You May Need:
- New parking brake cable
- Vehicle jack and jack stands
- Wrenches and sockets
- Pliers
- Screwdrivers
- Brake cable tensioning tool
- Replacement grommets or clips (if necessary)
- Brake cleaner
- Rust penetrant
- Safety equipment (gloves, safety glasses)
Procedure:
- Safety Precautions:
- Ensure the vehicle is on a flat and stable surface.
- Engage the parking brake and block the vehicle’s wheels to prevent it from rolling.
- Wear appropriate safety gear, including gloves and safety glasses.
- Lift the Vehicle:
- Use a vehicle jack to lift the rear of the vehicle and secure it with jack stands.
- Access the Cable:
- Locate the parking brake cable under the vehicle. Depending on your vehicle’s configuration, you may need to remove underbody panels or covers to access the cable.
- Release Tension:
- Release the tension on the parking brake cable by loosening the adjusting nut or bolt at the handbrake lever inside the vehicle’s cabin.
- Disconnect the Cable:
- Disconnect the parking brake cable from the rear brake calipers or drums. This may involve removing retaining clips or fasteners.
- Remove Old Cable:
- Trace the cable’s path and remove any clips or brackets that secure it to the vehicle’s chassis or body.
- Carefully remove the old parking brake cable from its routing.
- Install New Cable:
- Route the new parking brake cable through the same path as the old one.
- Secure the cable in place with clips or brackets, and make sure it follows the original routing.
- Connect to Rear Brakes:
- Reconnect the parking brake cable to the rear brake calipers or drums. Use new grommets or clips if necessary.
- Tension the Cable:
- Use a brake cable tensioning tool to adjust the cable tension. Consult your service manual for the proper tensioning procedure.
- Test the Brake:
- After connecting the cable, test the parking brake to ensure it engages and disengages correctly.
- Adjust the Handbrake Lever:
- Adjust the handbrake lever inside the vehicle to the appropriate tension.
- Check for Proper Operation:
- With the vehicle still safely raised on jack stands, ensure that the parking brake holds the vehicle securely in place.
- Lower the Vehicle:
- Once you’re satisfied with the cable installation and parking brake function, carefully lower the vehicle to the ground.
This is a general overview of the process to change the parking brake cable on a Mercedes W201. However, the specific steps and cable routing may vary based on your vehicle’s configuration and model year. It’s crucial to consult the vehicle’s service manual or seek professional assistance for precise instructions.
]]>Tools and Materials You May Need:
- Replacement wing mirror glass
- Flathead screwdriver
- Heat gun or hairdryer (for warming the adhesive)
- Razor blade or plastic trim tool
- Cleaning solution and a soft cloth
- Safety equipment (gloves, safety glasses)
Procedure:
- Safety Precautions:
- Ensure the vehicle is parked safely, the engine is turned off, and the handbrake is engaged.
- Wear safety gloves and glasses to protect your hands and eyes.
- Remove the Old Mirror Glass:
- Gently insert a flathead screwdriver or a plastic trim tool between the old mirror glass and the plastic housing. Be cautious not to damage the plastic housing.
- Apply gentle pressure and carefully pry the old mirror glass away from the housing.
- Warming the Adhesive:
- If the mirror glass is firmly attached, you can use a heat gun or a hairdryer to warm the adhesive on the back of the mirror. This will make it easier to remove. Be cautious not to overheat the glass or housing.
- Heat the adhesive by moving the heat source back and forth over the mirror’s surface. Do not focus the heat in one area for too long.
- Peel Off the Old Mirror Glass:
- After warming the adhesive, use a razor blade or plastic trim tool to gently lift and peel away the old mirror glass. Be careful not to scratch the plastic housing.
- Clean the Housing:
- Clean the plastic housing with a suitable cleaning solution and a soft cloth. Remove any remaining adhesive residue.
- Prepare the Replacement Glass:
- Ensure the replacement mirror glass is clean and free of any dust or debris. You can wipe it with a clean, dry cloth to be sure.
- Attach the Replacement Glass:
- Carefully position the replacement mirror glass onto the plastic housing, aligning the attachment points.
- Press the glass firmly to adhere it to the housing. Apply even pressure to ensure proper adhesion.
- Final Inspection:
- Carefully inspect the replacement mirror glass to ensure it’s securely attached and properly aligned within the housing.
- Test the Mirror:
- From inside the vehicle, test the mirror’s functionality by adjusting it to ensure it provides a clear and accurate reflection.
- Adjust the Mirror Position:
- Adjust the mirror to the desired position for optimal visibility.
Changing the mirror glass for the wing mirror on a Mercedes W201 is typically a straightforward process. However, it’s essential to exercise caution to avoid damaging the plastic housing or the new mirror glass during the replacement. If you’re uncertain about performing this task, or if your vehicle has specific features that make the process more complicated, consider seeking professional assistance.
]]>Tools and Materials You May Need:
- Replacement auxiliary indicator
- Screwdriver or a socket set
- Safety equipment (gloves, safety glasses)
Procedure:
- Safety Precautions:
- Ensure the vehicle is parked safely, the engine is turned off, and the handbrake is engaged.
- Wear safety gloves and glasses to protect your hands and eyes.
- Locate the Auxiliary Indicator:
- Identify the location of the auxiliary indicator on your Mercedes W201. On most models, this is typically located on the front fender, near the wheel well.
- Access the Bulb Housing:
- Depending on the specific design of your Mercedes 190, you may need to access the bulb housing from under the wheel well or by removing the inner fender liner. In some cases, you can access it directly from the engine bay.
- Remove the Bulb Housing:
- Using a screwdriver or a socket set, carefully remove the screws or bolts securing the bulb housing in place.
- Disconnect the Wiring:
- Gently disconnect the wiring harness connected to the auxiliary indicator. You may need to use a small flathead screwdriver to release any retaining clips.
- Remove the Old Indicator:
- Carefully detach the old auxiliary indicator from the bulb housing. It may have clips or tabs that secure it in place.
- Install the New Indicator:
- Align the new auxiliary indicator with the bulb housing and secure it by snapping it into place, making sure it fits securely.
- Reconnect the Wiring:
- Reconnect the wiring harness to the new auxiliary indicator. Ensure it clicks or locks into place.
- Reattach the Bulb Housing:
- Position the bulb housing back into place and secure it by reinserting and tightening the screws or bolts.
- Test the Indicator:
- Turn on your vehicle’s lights to test the new auxiliary indicator. Make sure it functions correctly, including both the parking and turn signal functions.
- Adjust the Indicator Position:
- If needed, adjust the new auxiliary indicator’s position to ensure it provides the proper angle and illumination.
- Final Inspection:
- Carefully inspect the auxiliary indicator to ensure it is securely attached, properly aligned, and functions correctly.
Changing the auxiliary indicator on a Mercedes W201 is generally a straightforward procedure, but it’s important to follow these steps carefully to ensure proper installation and function. If you’re unsure about performing this task, or if your vehicle has specific features that make the process more complicated, consider seeking professional assistance.
]]>- Choosing the Wrong Shock Absorbers:
- Selecting shock absorbers that are not compatible with your vehicle’s make and model can lead to handling and safety issues. Always use the correct shock absorbers for your specific vehicle to maintain ride quality and performance.
- Not Replacing Both Sides:
- Replacing only one shock absorber when both are worn or damaged can lead to uneven suspension and handling characteristics. It’s best to replace shock absorbers in pairs (either the front pair or the rear pair) to ensure balanced performance.
- Improper Installation:
- Failing to install the shock absorbers correctly can lead to performance problems and safety issues. Make sure to follow the manufacturer’s installation instructions and use the appropriate torque settings for mounting hardware.
- Neglecting Other Suspension Components:
- Shock absorbers are just one part of the suspension system. Neglecting to inspect and replace other worn or damaged suspension components like bushings, control arms, or struts can lead to suboptimal ride quality and handling.
- Not Performing a Wheel Alignment:
- After replacing shock absorbers, it’s essential to have a wheel alignment performed. Failing to do so can result in uneven tire wear, reduced handling, and alignment-related issues. Proper alignment ensures that all wheels are pointing in the right direction.
It’s crucial to take your time, follow the manufacturer’s instructions, and, if necessary, seek professional assistance when replacing shock absorbers. Proper installation and maintenance are essential for safety, ride quality, and the longevity of your vehicle’s suspension system.
]]>Tools and Materials You May Need:
- Rear brake caliper repair kit
- Brake fluid
- Brake cleaner
- Brake piston tool (for compressing the piston)
- Socket set
- Wrenches
- Screwdrivers
- Rubber mallet
- Brake bleeding kit
- Safety equipment (gloves, safety glasses)
Procedure:
- Safety Precautions:
- Ensure the vehicle is on a flat, stable surface, the engine is turned off, and the handbrake is engaged.
- Wear safety gloves and glasses to protect your hands and eyes.
- Lift the Vehicle:
- Lift the rear of the vehicle using a suitable jack and secure it with jack stands.
- Remove the Wheel:
- Remove the rear wheel to access the brake caliper.
- Brake Fluid Reservoir:
- Check the brake fluid reservoir and, if necessary, siphon off some brake fluid to prevent overflow when you compress the caliper piston.
- Disassemble the Brake Caliper:
- Carefully remove the brake caliper from its mounting bracket.
- Using the appropriate socket or wrench, disconnect the brake line from the caliper. Be prepared to catch any leaking brake fluid in a suitable container.
- Disassemble the caliper by removing the retaining bolts, pins, and any other hardware that holds it together.
- Remove the Old Seals and Piston:
- Carefully remove the old seals, o-rings, and piston from the caliper.
- Inspect the caliper components for wear or damage.
- Clean the Caliper:
- Thoroughly clean the caliper, including the caliper housing, piston bore, and all components. Use brake cleaner to remove any old brake fluid, dirt, and debris.
- Replace Seals and O-Rings:
- Install the new seals and o-rings from the repair kit into the caliper.
- Lubricate the new components with brake fluid before installation.
- Compress the Piston:
- Use a brake piston tool or a suitable tool to compress the caliper piston back into its bore. Ensure it’s flush with the caliper housing.
- Reassemble the Caliper:
- Reassemble the caliper, including all pins, bolts, and brackets, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Reattach the brake line and ensure it’s properly tightened.
- Bleed the Brakes:
- Bleed the brake system to remove any air. Starting with the furthest wheel from the master cylinder and working your way closer is a common method. Use a brake bleeding kit or ask someone to assist you.
- Refill Brake Fluid:
- Top off the brake fluid reservoir with fresh brake fluid and replace the cap.
- Test the Brake Pedal:
- Pump the brake pedal a few times to ensure the caliper piston seats properly.
- Check for any brake fluid leaks around the caliper.
- Replace the Wheel:
- Carefully reinstall the rear wheel and tighten the lug nuts.
- Lower the Vehicle:
- Carefully lower the vehicle to the ground.
- Test the Brakes:
- Test the brakes for proper operation by gently applying and releasing the pedal. Ensure there’s a firm brake pedal and that the vehicle stops correctly.
Rebuilding a rear brake caliper on a Mercedes W124 is a complex procedure that requires attention to detail and careful handling of brake components. If you’re not experienced with brake systems, it’s highly recommended to consult a professional mechanic or technician for assistance to ensure the job is done correctly and safely.
]]>Tools and Materials You May Need:
- Shock absorber and coil spring assembly (new)
- Spring compressors
- Socket set and wrenches
- Torque wrench
- Jack and jack stands
- Pry bar or ball joint separator
- Safety equipment (gloves, safety glasses)
Procedure:
- Safety Precautions:
- Ensure the vehicle is parked on a flat, stable surface, the engine is turned off, and the handbrake is engaged.
- Wear safety gloves and glasses to protect your hands and eyes.
- Raise the Vehicle:
- Lift the front or rear of the vehicle using a suitable jack and secure it with jack stands. Make sure the vehicle is safely supported.
- Remove the Wheel:
- Remove the wheel from the corner of the vehicle where you’ll be replacing the shock absorber and coil spring.
- Disconnect Components:
- Disconnect any components that attach to the shock absorber or coil spring, such as brake lines, ABS sensors, sway bar links, and the stabilizer bar, if present.
- Disconnect the Shock Absorber:
- Use a socket set and wrenches to disconnect the upper and lower mounting bolts or nuts for the shock absorber. This may require using a ball joint separator or a pry bar to free the lower control arm from the shock absorber.
- Remove the Coil Spring:
- Use a spring compressor tool to compress the coil spring, allowing you to remove it safely without tension. Carefully disconnect the coil spring from the upper and lower spring seats.
- Install the New Coil Spring:
- Place the new coil spring into the spring seats, ensuring it’s correctly positioned and aligned.
- Reconnect the Shock Absorber:
- Reattach the shock absorber to the vehicle’s suspension components, using the upper and lower mounting bolts or nuts. Make sure the shock absorber is securely in place.
- Reconnect Components:
- Reconnect any components you detached earlier, such as brake lines, ABS sensors, sway bar links, and the stabilizer bar.
- Tighten All Fasteners:
- Using a torque wrench, tighten all the mounting bolts and nuts to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Repeat for Other Side:
- If you’re replacing the shock absorbers and coil springs on both sides of the vehicle, repeat the above steps for the other side.
- Reinstall the Wheel:
- Carefully reinstall the wheel and tighten the lug nuts.
- Lower the Vehicle:
- Carefully lower the vehicle to the ground.
- Perform Alignment and Testing:
- After replacing the shock absorbers and coil springs, it’s essential to have a wheel alignment performed to ensure proper wheel alignment. Test the vehicle for proper suspension performance and handling characteristics.
Replacing shock absorbers and coil springs on a Mercedes W124 is a complex task and should be performed by experienced mechanics or technicians. Improper installation can affect the vehicle’s handling, safety, and ride comfort. If you’re not confident in your ability to perform this task, it’s highly recommended to seek professional assistance.
]]>